Meats and Sausages
Distillation Principles
Distillation equipment separates crude oil into diesel oil, kerosene, gasoline, naphtha and gas. Because all those components have different boiling temperatures, they can be separated by a process called fractional distillation. The same concept is employed for distilling alcohol from raw materials such as grains or potatoes. Distillation is a controlled process and alcohols of different strengths can be produced.
1. The first step of distillation is making a fermented mash. It is made from cheap materials such as grains or potatoes. In home production sugar is commonly used for the following reasons:
- It is relatively cheap and widely available.
- Ferments fast and produces alcohol rich mash.
- It does not produce bad odors.
- It is easy to clean the equipment and discard the leftover material.
- Sugar is mixed with water, fast working fermenting yeasts are added and the fermented mash is ready for distillation in a matter of days.
2. The mixture is brought to a boil and vapor is produced. This vapor consists of alcohol, water and aromatic substances.
3. The vapor flows into water cooled condenser where it liquefies becoming alcohol. Many people jump into making moonshine using simple pot still set up thinking that they will produce high quality strong alcohol. Well, it does not work this way. The simple traditional set up (alembic) consisting of a boiler and water condenser produces alcohol at an average strength of 32% depending on how rich in alcohol the fermenting mash is. In order to produce alcohol at about 90%, a single alembic must be used about nine times so the operation becomes impractical. However it is a suitable device for making fruit brandies.
Multi-stage distillation using traditional pot still
| Stage | The beginning | The end |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 11% (base alcohol, for example wine) | 32% |
| 2 | 32% | 55% |
| 3 | 55% | 70% |
| 4 | 70% | 78% |
| 5 | 78% | 83% |
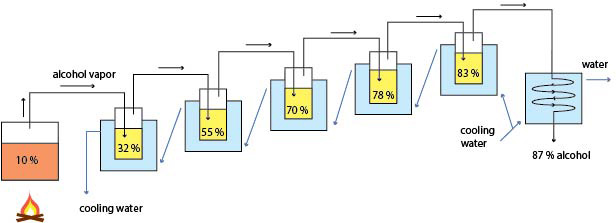
Multistage distillation principle.
The biggest alcohol strength increase is in the first and second stages. Then it starts to slow down. To go beyond 83% will require so many stages that the operation will be impractical. Today's equipment performs multistage distillation in one single operation in a single distillation column.
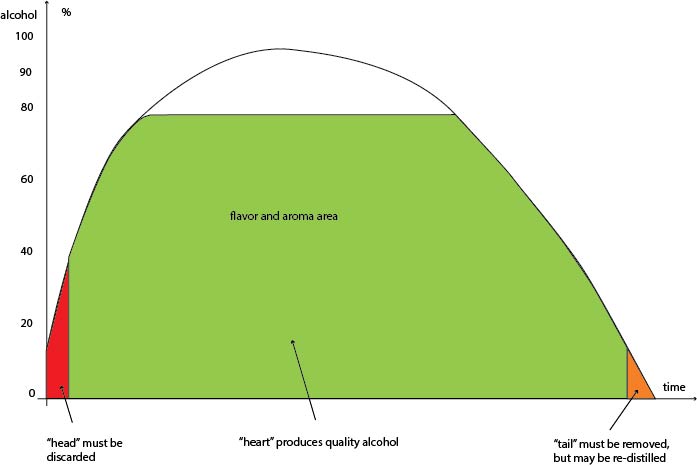
Different ranges of distillation, head, heart, tail, flavor range, pure alcohol.

















