Meats and Sausages
Canning Process
Canning high-acid foods such as jams, jellies, sauerkraut, kimchi, pickles, fermented vegetables, chutneys, and relishes is very easy, however, canning low-acid foods such as meat, poultry, fish and vegetables requires more knowledge. Low-acid recipes should be designed by processing authority and must be processed at higher temperatures in pressure canners. Please read Principles of Canning Low-Acid Foods and Microbiology and Safety of Canned Food.
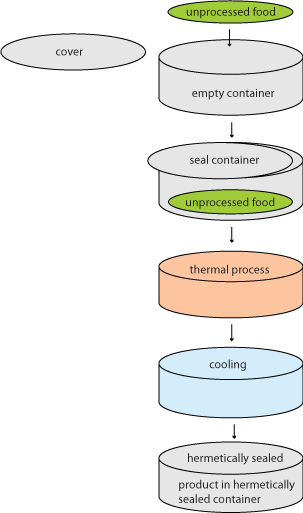
Canning process
The main steps in canning are:
- Packing the product into the container.
- Hermetically sealing the container. Hermetically sealed container means a container that is designed and intended to be secure against the entry of microorganisms and therefore maintains the commercial sterility of its contents after processing.
Thermally processing the product and the container together.
High-Acid foods are processed at 212° F, 100° C in water bath canner.
Low-Acid foods must be processed at 240 - 250° F, 116 - 121° C in pressure canner.
Cooling
Cooling foods which were processed in water bath canner is easy: remove the jars from the water bath canner and let them sit undisturbed to cool at room temperature from 12-24 hours. As the temperature of the product drops, a vacuum forms inside and pulls down the lid. This is often accompanied by a popping sound and happens within minutes after removing the jar from the water bath canner. The seal, however, is still soft and the cans must be left undisturbed for the seal to harden. Placing hot jar in cold water will crack the glass.
Cooling low acid-foods such as meat, poultry, fish and vegetables is more involved.
- Storage.
















