Meats and Sausages
Meat Cuts
Meat cuts can be divided into:
- Noble meat cuts.
- Less noble meat cuts.
Noble cuts are those cuts which chefs highly regard as:
- They consist almost entirely of desirable lean meat.
- Are easy to prepare as they contain small amounts of bone.
- Contain outside fat, which is easy to remove.
- Contain little connective tissue.
- Are simple to cook.
They are highly regarded by a consumer as:
- They can be cooked using simple methods.
- Are tender when cooked.
- Taste good.
Noble cuts come from the parts of the animal that exercise less frequently, such as beef round, rump, sirloin, loin or pork ham, loin, and belly. Less noble cuts exhibit opposite characteristics and come from the animal parts that frequently exercise, such as beef neck, chuck, shoulder, shin or pork shoulder, picnic, and hocks. Such cuts contain many bones, smaller muscles, and more connective tissue. As the animal carries a finite number of noble parts, the less noble and smaller parts are used for making sausages. This includes cuts and trimmings removed from the more noble cuts and parts such as the liver, kidney, heart, tongue, jowls, and skin. The only instance when noble meat cuts will be used for making sausages is the shortage of less noble cuts or a recipe such as ham sausage that calls specifically for lean ham.
There is a unique meat classification system in the USA:
- Acceptable grade - the only fresh pork sold in supermarkets.
- Utility grade - used in processed products and unavailable in supermarkets for purchase.
Short of being a farmer, living in a large city has little choice but to purchase meats in a local supermarket. Individuals who keep winning whole hog barbecue contests purchase their pigs from selected farmers.
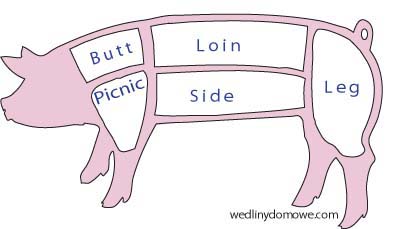
Pork meat is divided into five prime cuts:
- Shoulder butt (Boston butt).
- Shoulder picnic.
- Loin.
- Ham.
- Side (bacon, spare ribs).
Those main cuts are further broken down into additional parts. They all have unique names and numbers and are listed in a trade catalog. These five primary cuts are the meat a home sausage maker can purchase in a supermarket. Many meat products and known sausages require meats from other parts of the hog’s body than those five primary cuts mentioned above. To make liver sausages, you need liver, fat, meat from heads, brains, kidneys, hearts, back fat, lungs, tripes, etc. To make head cheese, you need head meat, shank (hocks) and skins.<,/p>
These parts are rich in collagen and will form a gelatin holding meat ingredients together. Blood is, of course, needed for blood sausages. Meat processors dealing with slaughterhouses have access to those meats, and they use them to manufacture different sausages. A person living on a farm will be able to obtain a hog without much difficulty; a person living in a large city faces some obstacles but can make substitutions.
These five primary cuts are the meat home sausagemakers can purchase in a supermarket. The best advice is to make friends with a local butcher.
There are seven USDA Beef Grades: Prime, Choice, Select, Standard, Commercial and Utility, Non-graded beef, and Natural beef. In addition, there are thirteen major steak names and several beef roasts.