Meats and Sausages
Meat Aging
When an animal dies, the oxygen stops flowing, and many reactions take place inside. For a few hours, the meat remains relaxed and may still be processed or cooked. Then muscles contract, and the meat stiffens, known as the “rigor mortis” stage. During that stage, which lasts differently for different animals, the meat should not be processed or cooked as the resulting product will be tough. Meat stock prepared from meats still in the rigor mortis stage is cloudy and has poor flavor. When this stage ends, the meat enters the "rigor" stage and is kept in a cooler. In time, it becomes tender again and is ready for processing. It is widely accepted that this happens due to changes in the protein structure. The length of rigor mortis or rigor stage directly depends on temperature. The higher the temperature, the shorter the stages, and vice versa. Make note that aging meat at high temperatures will help bacteria to grow and will adversely affect meat’s shelf-keeping qualities.
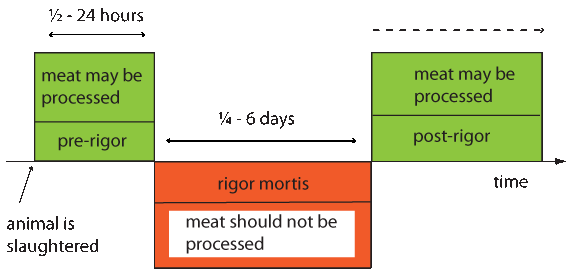
Effect of rigor mortis
Times for onset and resolution of rigor
| Animal | Time to onset of rigor | Time for resolution of rigor |
|---|---|---|
| Cattle | 12 - 24 hours | 2 - 10 days |
| Pig | 6 - 12 hours | 1 - 2 days |
| Lamb | 7 - 8 hours | 1 day |
| Turkey | 1/2 - 2 hours | 6 - 24 hours |
| Chicken | 1/2 - 1 hour | 4 - 6 hours |
| Rabbit | 12-20 hours | 2-7 days |
| Venison | 24 - 36 hours | 6 - 14 days |
Looking at the above data, it becomes conclusive that the aging process is more crucial for older animals at slaughter time (cattle, venison). Warm meat of a freshly slaughtered animal exhibits the highest quality and juiciness. Unfortunately, there is a very narrow window of opportunity for processing it. The slaughterhouse and the meat plant must be located within the same building to be effective. A packing house has already aged meat we buy in a supermarket. If an animal carcass is cooled too rapidly (below 50° F, 10° C) before the onset of the rigor (within 10 hours), the muscles may contract, resulting in tough meat when cooked. This is known as “cold shortening.” To prevent this, the carcass is kept at room temperature for some hours to accelerate rigor and then aged at between 30-41° F (-1 - 5° C).
















