Meats and Sausages
Solar Drying
Solar drying uses sun energy but is performed in a solar dryer designed and built for this purpose.
Solar food dryer is built to dry food using solar energy. Sunlight enters an enclosed chamber (sun collector) where it strikes a dark surface, converting its energy to heat. The heat dries the food. Airflow is accomplished by a natural draft (warm air rises), which can be controlled by adjusting vents. The same principle is used to control draft in a traditional smokehouse.
The sun collector and the drying chamber can be combined in one unit or separated. When the collector is free-standing, the heat it generates is directed into the drying chamber. Solar dehydrators may have backup electric heating to provide heat when the sun is not around.
Solar drying is an improved “open-air sun drying” method which offers significant benefits:
- Fast drying.
- Higher drying temperatures.
- Offers airflow and temperature control.
- Food is protected from elements.
The following drawing depicts one tray solar dryer.
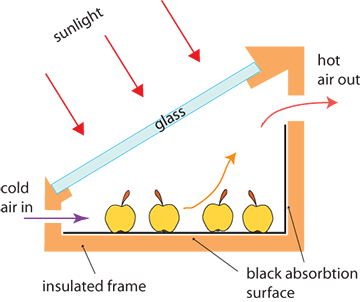
Solar dryer
The inside of the dryer is lined up with a black absorbing material or painted black. Cold air flows in at the bottom, but sun rays will heat the drying chamber and the air in it. Warm air rises and leaves the chamber. This natural airflow depends on the height difference (pressure) between fresh air intake and hot air exhaust. The bigger the difference, the faster the airflow.
The following drawing is a step-up design of the previous arrangement.
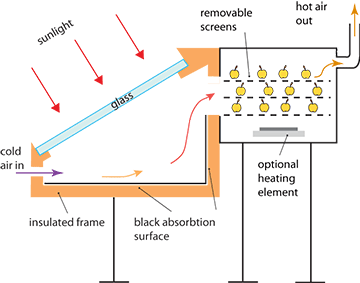
Solar dryer
The solar dryer works on sun energy during the day. The warming chamber supplies warm air to the drying chamber, containing three removable trays. At night, there is no significant drying, besides, there is a danger of condensation build-up as cold night air cannot hold much moisture. This will happen in hot and humid areas like Louisiana or Florida. The optional heating element can be switched on and the drying will continue through the night. The heating element can be placed in the warming chamber instead.
There is a pipe stack through which escapes warm and moist air. The higher the pipe, the bigger the difference in pressure between fresh air inlet and warm air exhaust. This results in a stronger airflow. The airflow and humidity can be controlled during drying by adjusting the air intake and pipe outlet. Thermometer and humidity sensor can be installed for more precise control.
Both devices, solar dryer and meat smokehouse, employ similar design features:
- Fresh air intake
- Smoke (hot air) exhaust
- Air flow
- Insulated frame
- Heating element
Using meat smokehouse to dry tomatoes. When drying tomatoes heating element supplies warm air. During smoking meat, burning wood alone or with the help of the heating element provides a warm temperature and smoke. In both cases the temperature of the air is around 60° C (140° F).

















